Activity Ratios: Know How Your Business Performs
Activity ratios are important indicators used to measure a company’s operational efficiency in utilizing its assets to generate revenue. By understanding various types of activity ratios, businesses can assess how effectively they are using their resources, such as inventory, receivables, and fixed assets. This article will discuss several key activity ratios, along with examples, to provide a clearer understanding of their calculation and application.
Understanding Activity Ratios
Activity ratios are a group of financial metrics used to evaluate how efficiently a company is using its assets to run operations and generate sales. These ratios assess the speed at which assets like inventory and receivables are converted into cash or revenue. They are essential for monitoring how well a company manages its resources and can provide insight into management’s ability to maximize asset utilization.
Also read:Price to Book Value: Is Your Stock Overvalued?
Types of Activity Ratios
1. Receivables Turnover Ratio
The receivables turnover ratio measures how quickly a company can collect payments from its accounts receivable. This ratio indicates the efficiency of the company’s credit policies and its ability to manage credit extended to customers. The formula is:
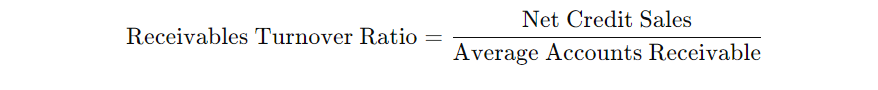
Example:
Suppose a company has net credit sales of $500,000 for a year and an average accounts receivable balance of $100,000. The receivables turnover ratio would be:
$500,000/$100,000=5
This means the company collects its receivables five times a year. A higher ratio suggests that the company efficiently collects its outstanding receivables, signaling strong credit management.
2. Inventory Turnover Ratio
The inventory turnover ratio measures how quickly a company sells its inventory over a specific period. This ratio is crucial for businesses that rely heavily on inventory because holding too much stock can lead to higher storage costs or obsolescence. The formula is:
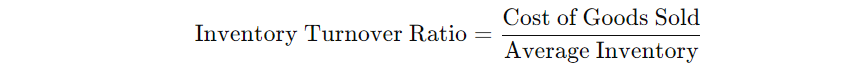
Example:
If a company’s cost of goods sold (COGS) for the year is $800,000, and the average inventory held is $200,000, the inventory turnover ratio would be calculated as:
$800,000/$200,000=4
This means the company sells and replenishes its inventory four times a year. A higher ratio indicates better inventory management and faster sales cycles.
3. Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
The fixed asset turnover ratio assesses how efficiently a company uses its fixed assets, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, to generate revenue. This ratio helps determine whether the investment in fixed assets is producing adequate returns. The formula is:
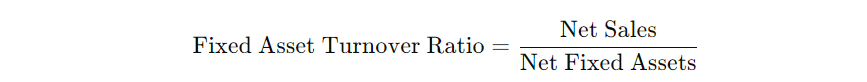
Example:
Assume a company generates $1,000,000 in net sales and has net fixed assets worth $500,000. The fixed asset turnover ratio would be:
$1,000,000/$500,000=2
This indicates that for every dollar invested in fixed assets, the company generates two dollars in sales. A higher ratio shows that the company is using its fixed assets efficiently to drive revenue.
Also read:Internal Rate of Return: Know Your Profit Goal
Importance of Understanding Activity Ratios
Activity ratios are crucial because they provide insight into a company’s operational efficiency. By regularly monitoring these ratios, management can identify areas where the company may need to improve its resource utilization, such as better inventory management, faster receivables collection, or more effective use of fixed assets.
Avoiding Operational Issues
If a company has a low receivables turnover ratio, it may indicate that it is having trouble collecting payments from customers. Similarly, a low inventory turnover ratio could suggest that the company is holding onto unsold stock for too long, increasing storage costs and reducing profitability. Therefore, it’s important for management to regularly review these ratios to ensure efficient operations.
Limitations of Activity Ratios
Although activity ratios are useful tools, there are limitations to their use. First, these ratios often rely on historical data and may not accurately predict future performance. Second, the financial figures used in ratio calculations can be affected by the accounting methods a company employs, such as depreciation policies or inventory accounting methods. Therefore, while these ratios provide valuable insights, they should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics when making decisions.
Conclusion
Activity ratios are essential tools for measuring a company’s efficiency in utilizing its assets to generate revenue. By understanding the various types of activity ratios, businesses can evaluate areas where improvements may be needed and enhance their overall performance. Additionally, these ratios provide valuable insights for investors looking to assess a company’s ability to manage its resources effectively. A solid understanding of these metrics can help management and investors make more informed decisions and ultimately increase the company’s value.
Also read:Price to Earnings and Its Importance for Investors

References
Corporate Finance Institute. (n.d.). Activity Ratios. https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/accounting/activity-ratios/
Investopedia. (n.d.). Activity Ratio. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/activityratio.asp
Invesnesia. (n.d.). Rasio Aktivitas: Pengertian, Rumus, Jenis, dan Contoh Perhitungan. https://www.invesnesia.com/rasio-aktivitas
Wall Street Mojo. (n.d.). Activity Ratios. https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/activity-ratios/







